Vitamin D Deficiency Complications: Risks, Symptoms & Treatments
Uncover the serious health complications of Vitamin D deficiency, from bone weakening to immune dysfunction. Learn key symptoms, risk factors, and effective treatment options to boost your Vitamin D.
Patients with a prolonged and severe vitamin D deficiency can experience symptoms associated with secondary hyperparathyroidism including bone pain, arthralgia’s, myalgia’s, fatigue, muscle twitching (fasciculation’s), and weakness. Fragility fractures may result from chronic vitamin D deficiency leading to osteoporosis. A medical professional is best able to provide information about your particular circumstances. If you need immediate assistance, please call emergency services.
Unveiling the Shadows: Understanding the Complications of Vitamin D Deficiency
Introduction
In the realm
of human health, the significance of vitamins cannot be overstated. Among
these, vitamin D stands out as a crucial nutrient that plays a multifaceted
role in maintaining overall health. It is more than just a vitamin; it
functions as a hormone influencing an array of physiological processes in the
body. However, deficiency in this vital nutrient has gained attention due to
its potential to cause a wide range of health complications. Despite its
importance, a significant portion of the global population experiences a
deficiency in this essential vitamin. In this article, we delve into the
intricacies of vitamin D, its sources, functions, and the profound
complications arising from its deficiency.
Understanding Vitamin D: Sources and Functions
Vitamin D,
often referred to as the "sunshine vitamin," is unique among
other vitamins due to its ability to be synthesized within the body in response
to sunlight exposure. Ultraviolet B (UVB) rays from the sun interact with the
skin to produce vitamin D. Additionally, it can be obtained through dietary
sources such as fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), fortified foods (milk, orange
juice, cereals), and supplements.
The primary
function of vitamin D is the regulation of calcium and phosphate
metabolism, pivotal for maintaining bone health. It aids in the absorption of
calcium from the intestines and supports its incorporation into bones, thus
promoting bone mineralization. Furthermore, it plays a significant role in
modulating the immune system, promoting cell growth, reducing inflammation, and
influencing neuromuscular and cardiovascular functions.
Complications Arising from Vitamin D Deficiency
The
repercussions of vitamin D deficiency extend beyond weakened bones and manifest
in various bodily systems. Understanding these complications underscores the
gravity of ensuring adequate vitamin D levels for optimal health.
1- Bone Health and Rickets
Perhaps the most well-known consequence of vitamin D deficiency is
its impact on bone health. In children, a severe deficiency can lead to
rickets, a condition characterized by soft, weak bones, skeletal deformities,
stunted growth, and an increased risk of fractures. In adults, a lack of
vitamin D contributes to osteomalacia, causing bone pain, muscle weakness, and
an increased susceptibility to fractures.
2- Increased
Risk of Osteoporosis
A chronic
deficiency in vitamin D significantly raises the risk of osteoporosis, a
condition where bones become brittle and fragile due to reduced bone density.
This condition heightens the likelihood of fractures, especially in the hip,
spine, and wrist.
3- Muscle
Weakness and Pain
Vitamin D
deficiency is associated with muscle weakness and pain, contributing to a
higher risk of falls, decreased physical performance, and a general sense of
fatigue. Proper vitamin D levels are crucial for maintaining muscle strength
and function.
4- Immune System
Dysfunction
Vitamin D
plays a pivotal role in modulating the immune system. Deficiency has been
linked to an increased susceptibility to infections, autoimmune diseases, and a
compromised ability to fight off illnesses.
5- Cardiovascular
Complications
Research
suggests that low levels of vitamin D may be associated with an increased risk
of cardiovascular diseases, including hypertension, heart disease, and stroke.
Its deficiency may contribute to factors such as high blood pressure,
inflammation, and arterial stiffness.
6- Mental Health
Implications
Emerging
studies have indicated a potential link between vitamin D deficiency and
certain mental health conditions. Low levels of vitamin D have been associated
with depression, seasonal affective disorder (SAD), and cognitive impairment.
7- Increased
Cancer Risk
While the
exact relationship is still under investigation, some studies have suggested
that inadequate levels of vitamin D might contribute to an increased risk of
certain cancers, including breast, prostate, and colon cancers.
Addressing and Preventing Vitamin D Deficiency
Recognizing
the potential complications arising from vitamin D deficiency highlights the importance
of prevention and adequate supplementation.
1. Sun Exposure:
Safely exposing the skin to sunlight is a natural way to boost vitamin D
levels. However, caution is necessary to avoid overexposure and the risk of
skin damage. Balance is key; aiming for around 10-30 minutes of sunlight
exposure a few times a week on bare skin can help in synthesizing vitamin D.
2. Dietary
Sources: Consuming foods rich in vitamin D such as
fatty fish, fortified dairy products, and egg yolks can contribute to
maintaining adequate levels. However, it might be challenging to obtain
sufficient vitamin D through diet alone.
3. Supplements:
In cases where sunlight exposure and dietary sources are insufficient,
supplements are recommended. Consulting with a healthcare professional to
determine the appropriate dosage is crucial, as excess vitamin D can also lead
to adverse health effects.
4. Regular
Testing: Periodic testing to measure blood levels
of vitamin D assists in determining if supplementation is necessary. Optimal
levels may vary depending on individual health conditions and geographic
location.
Complications of Vitamin D deficiency include
Rickets:
A rare disease that causes thin, weak, and deformed bones in children.
Osteoporosis:
A loss of bone density in adults that can lead to fractures.
Secondary
hyperparathyroidism: Symptoms include bone pain, arthralgias,
myalgia’s, fatigue, muscle twitching (fasciculation’s), and weakness.
Fragility
fractures: Can result from chronic vitamin D
deficiency leading to osteoporosis
Low blood
calcium levels (Hypocalcemia)
·
Low blood phosphate levels
·
Depression
·
Impaired cognitive function
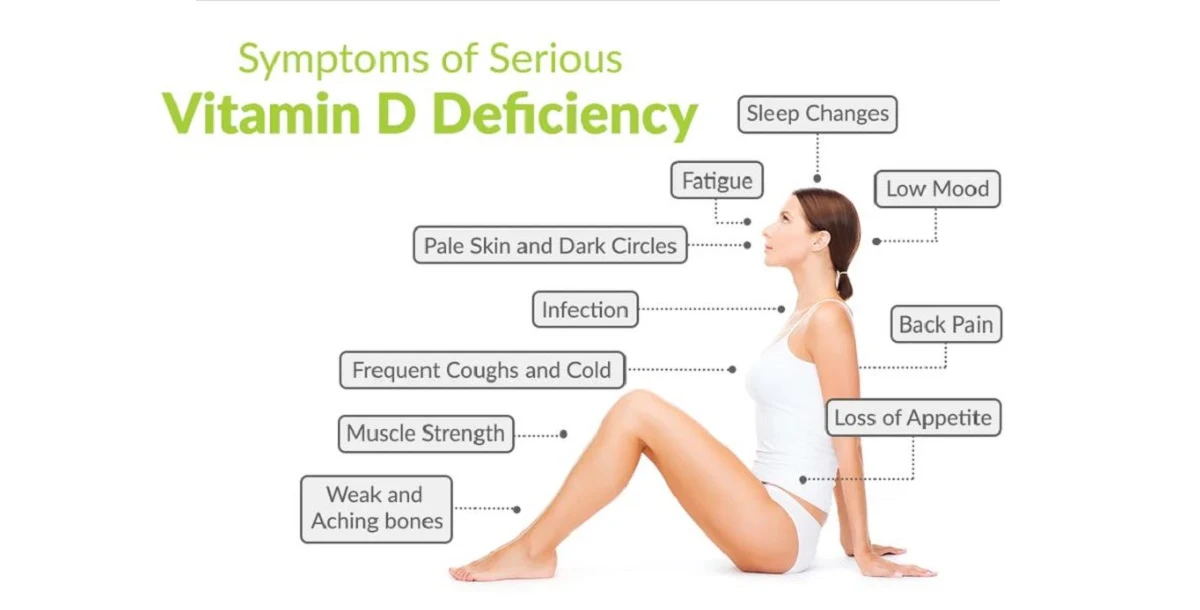
Other signs of Vitamin D deficiency include
·
Getting illnesses or
infections more often
·
Feeling tired or fatigued
·
Hair loss
·
Muscle pain
·
Lower back pain
·
Feelings of depression or low
mood
·
Wounds that heal slowly
following surgery, infection or injury
Conclusion
Vitamin D
deficiency represents a significant public health
concern due to its widespread prevalence and its far-reaching implications for
overall health. The complications arising from a lack of this essential
nutrient encompass various bodily systems, affecting bone health, immune function,
cardiovascular health, and mental well-being. Awareness, preventive measures,
and early intervention are key in mitigating the risks associated with vitamin
D deficiency. By fostering a deeper understanding of the importance of this
vital nutrient, individuals and healthcare providers can work together to
ensure adequate vitamin D levels, thereby promoting better health and
well-being for all.
FAQ
What happens
when you have low vitamin D?
What are the
complications of vitamin D deficiency in children?
Tags
14 Signs Of
Vitamin D Deficiency, Weird Symptoms Of Vitamin D Deficiency, How Long Does It
Take To Recover From Vitamin D Deficiency, Causes Of Vitamin D Deficiency, Vitamin
D Deficiency Cancer Symptoms, Vitamin D Deficiency Causes Which Disease, Low
Vitamin D Symptoms Female, Vitamin D Deficiency Self-Care
Follow us @
#Pinterest, #LinkedIn, #FcBk, #X, #FBPage, #Tele, #GovJob, #Awareness, #Information, #HealthiFashion, #OldPapers, #Insta







Post a Comment